Marquisette is a sheer, lightweight mesh or net fabric with a leno weave. It can be made from almost any fibre: silk, cotton, wool, rayon, nylon, polyester and a blend of any of the above. It is used for dresses, curtains, and mosquito netting. It is very similar to grenadine, but with a slightly more open weave. Marquisette can look quite different depending on the fibres used and variants and finished applied to the weave.

Leno weave - figure 8 threads twining around straight threads
Finding images of antique dresses made of marquisette is problematic as few museums and garment sellers look at the fabric closely enough (you need to inspect it under a very strong magnifying glass to see the weave) to correctly label marquisette. Many extent 19teens gowns probably include marquisette, but are not labelled as such.

Wedding dress (detail), 1910 US, Kent State. Is that material marquisette? Likely, but impossible to tell for sure.
The earliest mention I can find for marquisette is an ad for wool and silk ‘box robes’ in 1907, but the term is in quotation marks, indicating that it is still a new and novel word. This must be one of the earliest usages of the term, as the Merriam-Webster dates it to 1908 (and yeah, I totally had a textile historian happy geek moment when I realised I had found an earlier usage!).
By 1908 the term appears all over the place. Marquisette is sold, along with voile, as a ‘robing’ fabric, and promoted as an excellent fabric for evening gowns when traveling. Note that the descriptions of marquisette as a ‘robing fabric’ or ‘robing lengths’ didn’t mean it was to be used for bathrobe/kimono type garments, but for draping or ‘robing’ over other dresses.
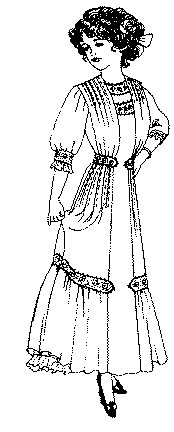
It was a common fabric for scarves, evening dresses, wedding and bridesmaid dresses throughout the 1910s. Fashion columns from 1911, in particular mention marquisette as the perfect light, limp fabric for the newly fashionable Directorie look, particularly for evening wear. At this time it was made mostly in silk, cotton, wool and rayon, making it very light and draping. Three of these Deliniator designs from 1911, for example, recommend marquisette as a fabric.

Fashions from The Delineator, 1911 - the white dress is a perfect example of a dress that could be made in marquisette
Past patterns carries a pattern for a misses dress with marquisette as one of the suggested fabrics.
Past Pattern #4971- Misses' Panel Dress- Circa 1910-1911
In the late teens and 1920s its usage broadened to include daywear, and began to loose a bit of its glamour as the name was applied to net curtains.
It remained a popular fabric for evening wear throughout the 1920s, 30s & 40s, suiting the soft, romantic gowns in vogue. Manufacturers started to make it in nylon and other synthetics, resulting in a much stiffer, crisper, organdy-like fabric than the early ‘teens variants.

McCall 9153. Jr Miss Eve Dress. "Nicest made in something bth stiff and sheer-mousseline, organdy, marquisette or net."
By late the 30s marquisette is seen almost exclusively in descriptions of window coverings and underskirts, though a few brides carried on wearing it. Was this just because wedding fashions tend to be quite old-fashioned? Or because rationing meant that fancy silk marquisettes weren’t readily available, and people were saving for really special events ?
That would explain the resurgence of marquisette in the 1950s, when the stiff variants perfectly suited full skirted dresses, and were used both for trimming, and as an interlining to hold out skirts.

1950s dress described as being of marquisette, Vintageous.com
Marquisette is still available today: the leno weave makes it very stable, so it is frequently used in bra construction. In cotton it is a very soft weave, so is seen in baby blankets. It also turns up in fabric stores, but not always under the label of marquisette.
So what is it made out of?
Apparently, everything and anything. In 1911 it is wool. An ad from 1912 describes it as being made of art silk and cotton, while a 1915 ad shows it in all cotton and seems to indicate it is a type of voile.
And was marquisette really the same thing we mean by it today in its earliest incarnations? It is described as a it voile, and then a bengaline, and then something with a silky finish? If it is mesh (per the modern meaning) how exactly was it striped, as described in a 1908 ad? Possibly terms like ‘marquisette voile’, and ‘bengaline marquisette’ indicated the fibres it was woven out of. Or perhaps marquisette was used as a generic term for a very light, draping gauzy fabric by ad writers who didn’t know the technical definition.
So what should Tara use as a modern alternative to marquisette? Well, it looks like there are occasionally silk marquisette fabrics on the market, but they may not be labelled as such, and they may be the crisper organdy-style marquisettes, rather than a limp marquisette as was fashionable in 1911. And most of the time you’d need a magnifying glass too see if the weave were right! If it were me, I’d go for a silk net, such as the one I used for the 1912 laurel dress, or a very fine silk gauze, preferably with a weave that is slightly more interesting than a tabby weave.

The 1912 Laurel Dress
Want to know even more? Joan Kipler has written an excellent article on marquisette and grenadine for fabrics.net.




















